Knee Replacement
Joint Replacement
Arthritic or damaged bones surfaces are removed and resurfaced with an artificial joint known as prosthesis. Knee and hip replacements are most common, but joint replacement can be performed on other joint such as the shoulder, elbow, etc.
Why Joint Replacement is necessary?
When complete joint is damaged with degenerated cartilage all over then it becomes difficult for the patient to continue day to day activities of life. So total joint replacement to be considered if other options like medication, physiotherapy etc will not relieve pain and disability in such condition. The goal is to relieve the pain in the joint caused by the damage done to the cartilage.
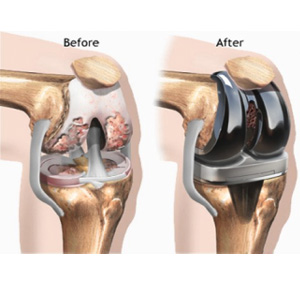
Total Knee Replacement
When whole knee joint (all compartments) is affected then only solution to relieve pain and get back to normal routine activities is total knee replacement surgery. In this procedure thigh bone side of joint (femur) is replaced with metal prosthesis, leg side (tibia) is replaced with metal and plastic and knee cap (patella) is replaced with plastic prosthesis. Results and durability of this surgery is excellent.
Unicondylar Knee Replacement
When one compartment of knee joint is arthritic then replacing this part with metal and plastic joint through a small incision (skin cut) provides excellent quick recovery. Benefit of this operation is that patient can bend the knee fully and can perform most of the activities.
When Surgery Is Recommended
There are several reasons why your doctor may recommend knee replacement surgery. People who benefit from total knee replacement often have:
- Severe knee pain or stiffness that limits your everyday activities, including walking, climbing stairs, and getting in and out of chairs
- Moderate or severe knee pain while resting, either day or night
- Chronic knee inflammation and swelling that does not improve with rest or medications
- Knee deformity — a bowing in or out of your knee
- Failure to substantially improve with other treatments such as anti-inflammatory medications, cortisone injections, lubricating injections, physical therapy, or other surgeries